← 上一章:反思 | 返回目录 | 下一章:规划 →
第五章:工具使用(函数调用)
工具使用模式概述
到目前为止,我们讨论的智能体模式主要涉及编排语言模型之间的互动,以及管理信息在智能体内部工作流程中的流动(链式调用、路由、并行化、反思)。然而,要让智能体真正有用并与现实世界或外部系统互动,它们需要具备使用工具的能力。
工具使用模式,通常通过一种称为函数调用的机制实现,使智能体能够与外部 API、数据库、服务进行交互,甚至执行代码。它允许作为智能体核心的 LLM 根据用户的请求或任务的当前状态,决定何时以及如何使用特定的外部函数。
这个过程通常包括:
- 工具定义(Tool Definition): 外部函数或能力被定义并描述给 LLM。这种描述包括函数的目的、名称以及它接受的参数,以及它们的类型和描述。
- LLM 决策(LLM Decision): LLM 接收到用户的请求和可用的工具定义。基于它对请求和工具的理解,LLM 决定是否需要调用一个或多个工具来完成请求。
- 函数调用生成(Function Call Generation): 如果 LLM 决定使用工具,它会生成一个结构化输出(通常是 JSON 对象),指定要调用的工具名称以及从用户请求中提取的要传递给它的参数。
- 工具执行(Tool Execution): 智能体框架或编排层拦截这个结构化输出。它识别请求的工具,并使用提供的参数执行实际的外部函数。
- 观察/结果(Observation/Result): 工具执行的输出或结果返回给智能体。
- LLM 处理(可选但常见): LLM 接收工具的输出作为上下文,并利用它来制定对用户的最终响应,或决定工作流程中的下一步(这可能涉及调用另一个工具、反思或提供最终答案)。
这种模式至关重要,因为它打破了 LLM 训练数据的局限性,使其能够访问最新信息,执行它内部无法完成的计算,与用户特定数据互动,或触发现实世界的动作。函数调用是一种技术机制,它弥合了 LLM 的推理能力与大量可用的外部功能之间的差距。
尽管“函数调用”恰当地描述了调用特定、预定义代码函数的行为,但我们有必要考虑更具扩展性的“工具调用”概念。这个更宽泛的术语承认智能体的能力可以远远超出简单的函数执行。一个“工具”可以是一个传统函数,但它也可以是一个复杂的 API 端点、对数据库的请求,甚至是针对另一个专业智能体的指令。这种视角使我们能够设想出更复杂的系统,例如,一个主智能体可能会将一项复杂的数据分析任务委托给一个专门的“分析师智能体”,或通过其 API 查询外部知识库。从“工具调用”的角度思考,能更好地捕捉智能体作为数字资源和其它智能实体多样化生态系统的协调者的全部潜力。
像 LangChain、LangGraph 和 Google Agent Developer Kit (ADK) 这样的框架为工具的定义和集成到智能体工作流程中提供了强大的支持,它们通常利用现代 LLM(如 Gemini 或 OpenAI 系列中的模型)的原生函数调用能力。在这些框架的“画布”上,你定义了工具,然后配置智能体(通常是 LLM 智能体)以使其知晓并能够使用这些工具。
工具使用是构建强大、交互式和具备外部感知能力的智能体的基石模式。
实际应用和用例
工具使用模式适用于智能体需要超越文本生成,执行动作或检索特定动态信息的几乎所有场景:
1. 从外部源检索信息:
访问 LLM 训练数据中不存在的实时数据或信息。
- 用例: 一个天气智能体。
- 工具: 一个天气 API,接收地点并返回当前天气情况。
- 智能体流程: 用户问:“伦敦的天气怎么样?”,LLM 识别需要使用天气工具,使用“伦敦”调用工具,工具返回数据,LLM 将数据格式化为用户友好的响应。
2. 与数据库和 API 交互:
对结构化数据执行查询、更新或其它操作。
- 用例: 一个电商智能体。
- 工具: 检查产品库存、获取订单状态或处理付款的 API 调用。
- 智能体流程: 用户问:“产品 X 有库存吗?”,LLM 调用库存 API,工具返回库存数量,LLM 告诉用户库存状态。
3. 执行计算和数据分析:
使用外部计算器、数据分析库或统计工具。
- 用例: 一个金融智能体。
- 工具: 一个计算器函数、一个股票市场数据 API、一个电子表格工具。
- 智能体流程: 用户问:“AAPL 的当前价格是多少,如果我以 150 美元买入 100 股,潜在利润是多少?”,LLM 调用股票 API,获取当前价格,然后调用计算器工具,得到结果,格式化响应。
4. 发送通讯:
发送电子邮件、消息,或向外部通讯服务进行 API 调用。
- 用例: 一个个人助理智能体。
- 工具: 一个发送邮件的 API。
- 智能体流程: 用户说:“给 John 发邮件,关于明天的会议。”,LLM 调用邮件工具,参数为从请求中提取的收件人、主题和正文。
5. 执行代码:
在安全环境中运行代码片段以执行特定任务。
- 用例: 一个编程助手智能体。
- 工具: 一个代码解释器。
- 智能体流程: 用户提供一个 Python 代码片段并问:“这段代码是做什么的?”,LLM 使用解释器工具运行代码并分析其输出。
6. 控制其它系统或设备:
与智能家居设备、物联网平台或其它连接系统交互。
- 用例: 一个智能家居智能体。
- 工具: 一个控制智能灯光的 API。
- 智能体流程: 用户说:“关掉客厅的灯。” LLM 调用智能家居工具,参数为指令和目标设备。
工具使用是将语言模型从一个文本生成器转变为一个能够在数字或物理世界中感知、推理和行动的智能体的关键(见图 1)。
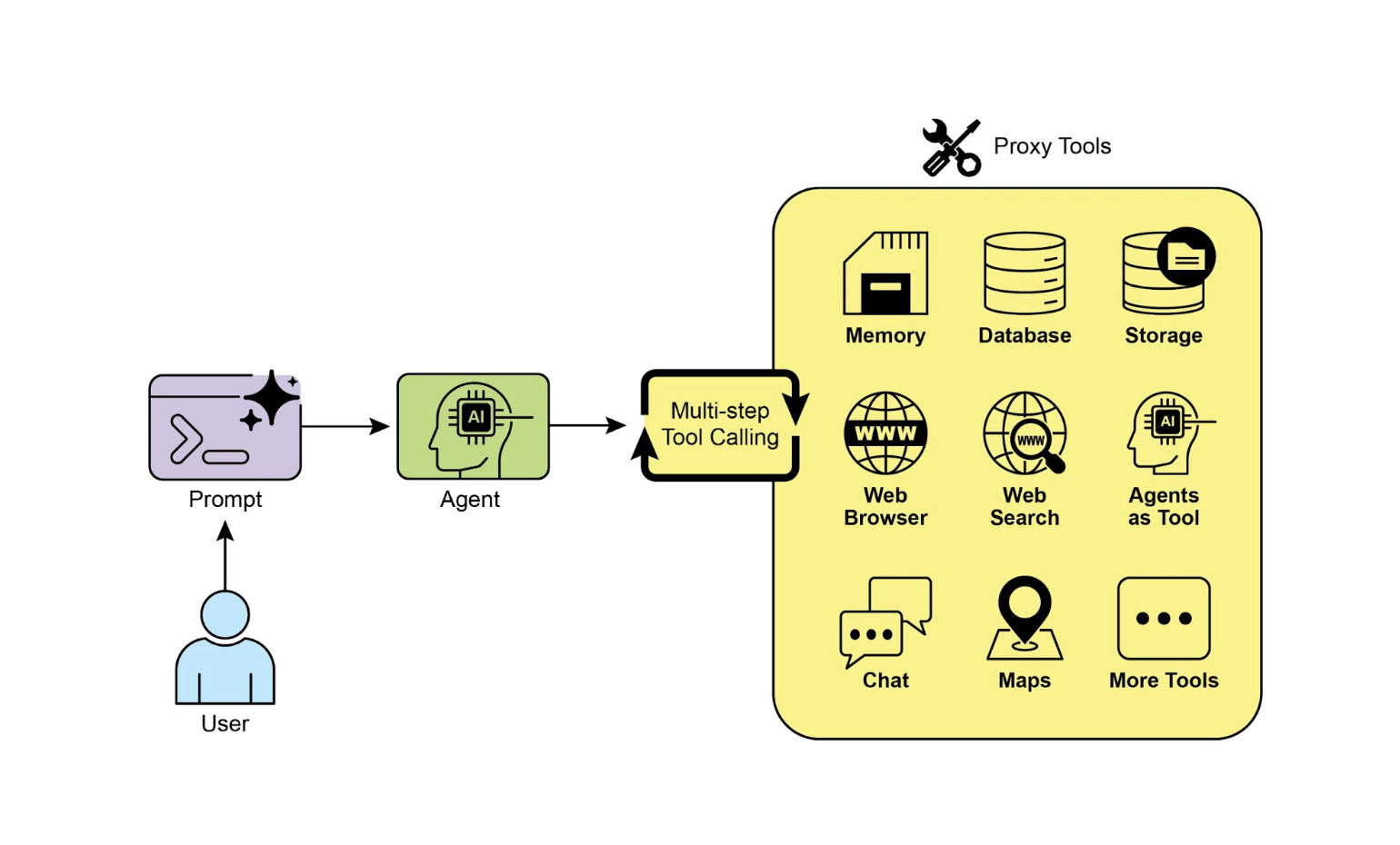
图 1:智能体使用工具的一些例子
动手代码示例 (LangChain)
在 LangChain 框架内实现工具使用是一个两阶段过程。首先,定义一个或多个工具,通常是通过封装现有的 Python 函数或其它可运行组件。随后,将这些工具绑定到一个语言模型上,从而赋予模型在判断需要外部函数调用来完成用户查询时,生成结构化工具使用请求的能力。
下面的实现将通过首先定义一个模拟信息检索工具的简单函数来演示这个原理。然后,将构建一个智能体并对其进行配置,使其能够响应用户输入而利用这个工具。执行此示例需要安装核心 LangChain 库和一个特定于模型的提供商包。此外,与所选语言模型服务进行适当的身份验证,通常是通过在本地环境中配置 API 密钥,是必要的先决条件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| import os, getpass
import asyncio
import nest_asyncio
from typing import List
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import logging
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.tools import tool as langchain_tool
from langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutor
# UNCOMMENT
# Prompt the user securely and set API keys as an environment variables
os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter your Google API key: ")
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter your OpenAI API key: ")
try:
# A model with function/tool calling capabilities is required.
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-2.0-flash", temperature=0)
print(f"✅ Language model initialized: {llm.model}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"🛑 Error initializing language model: {e}")
llm = None
# --- Define a Tool ---
@langchain_tool
def search_information(query: str) -> str:
"""
Provides factual information on a given topic. Use this tool to find answers to phrases
like 'capital of France' or 'weather in London?'.
"""
print(f"\n--- 🛠️ Tool Called: search_information with query: '{query}' ---")
# Simulate a search tool with a dictionary of predefined results.
simulated_results = {
"weather in london": "The weather in London is currently cloudy with a temperature of 15°C.",
"capital of france": "The capital of France is Paris.",
"population of earth": "The estimated population of Earth is around 8 billion people.",
"tallest mountain": "Mount Everest is the tallest mountain above sea level.",
"default": f"Simulated search result for '{query}': No specific information found, but the topic seems interesting."
}
result = simulated_results.get(query.lower(), simulated_results["default"])
print(f"--- TOOL RESULT: {result} ---")
return result
tools = [search_information]
# --- Create a Tool-Calling Agent ---
if llm:
# This prompt template requires an `agent_scratchpad` placeholder for the agent's internal steps.
agent_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful assistant."),
("human", "{input}"),
("placeholder", "{agent_scratchpad}"),
])
# Create the agent, binding the LLM, tools, and prompt together.
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, tools, agent_prompt)
# AgentExecutor is the runtime that invokes the agent and executes the chosen tools.
# The 'tools' argument is not needed here as they are already bound to the agent.
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, verbose=True, tools=tools)
async def run_agent_with_tool(query: str):
"""Invokes the agent executor with a query and prints the final response."""
print(f"\n--- 🏃 Running Agent with Query: '{query}' ---")
try:
response = await agent_executor.ainvoke({"input": query})
print("\n--- ✅ Final Agent Response ---")
print(response["output"])
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n🛑 An error occurred during agent execution: {e}")
async def main():
"""Runs all agent queries concurrently."""
tasks = [
run_agent_with_tool("What is the capital of France?"),
run_agent_with_tool("What's the weather like in London?"),
run_agent_with_tool("Tell me something about dogs.") # Should trigger the default tool response
]
await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
nest_asyncio.apply()
asyncio.run(main())
|
这段代码使用 LangChain 库和 Google Gemini 模型设置了一个工具调用智能体。它定义了一个 search_information 工具,模拟为特定查询提供事实性答案。该工具对 “weather in london”、“capital of france” 和 “population of earth” 预设了响应,并对其他查询有一个默认响应。代码初始化了一个 ChatGoogleGenerativeAI 模型,确保其具备工具调用能力。创建了一个 ChatPromptTemplate 来指导智能体的交互。create_tool_calling_agent 函数用于将语言模型、工具和提示组合成一个智能体。然后设置了一个 AgentExecutor 来管理智能体的执行和工具调用。定义了 run_agent_with_tool 异步函数,用给定查询调用智能体并打印结果。主异步函数 main 准备了多个查询以并发运行。这些查询旨在测试 search_information 工具的特定响应和默认响应。最后,asyncio.run(main()) 调用执行所有智能体任务。代码包含对 LLM 成功初始化的检查,然后才进行智能体设置和执行。
动手代码示例 (CrewAI)
这段代码提供了一个如何在 CrewAI 框架中实现函数调用(工具)的实际示例。它设置了一个简单场景,其中一个智能体配备了一个信息查找工具。该示例特别演示了使用这个智能体和工具来获取一个模拟的股票价格。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
| # pip install crewai langchain-openai
import os
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew
from crewai.tools import tool
import logging
# --- Best Practice: Configure Logging ---
# A basic logging setup helps in debugging and tracking the crew's execution.
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
# --- Set up your API Key ---
# For production, it's recommended to use a more secure method for key management
# like environment variables loaded at runtime or a secret manager.
#
# Set the environment variable for your chosen LLM provider (e.g., OPENAI_API_KEY)
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
# os.environ["OPENAI_MODEL_NAME"] = "gpt-4o"
# --- 1. Refactored Tool: Returns Clean Data ---
# The tool now returns raw data (a float) or raises a standard Python error.
# This makes it more reusable and forces the agent to handle outcomes properly.
@tool("Stock Price Lookup Tool")
def get_stock_price(ticker: str) -> float:
"""
Fetches the latest simulated stock price for a given stock ticker symbol.
Returns the price as a float. Raises a ValueError if the ticker is not found.
"""
logging.info(f"Tool Call: get_stock_price for ticker '{ticker}'")
simulated_prices = {
"AAPL": 178.15,
"GOOGL": 1750.30,
"MSFT": 425.50,
}
price = simulated_prices.get(ticker.upper())
if price is not None:
return price
else:
# Raising a specific error is better than returning a string.
# The agent is equipped to handle exceptions and can decide on the next action.
raise ValueError(f"Simulated price for ticker '{ticker.upper()}' not found.")
tools = [get_stock_price]
# --- 2. Define the Agent ---
# The agent definition remains the same, but it will now leverage the improved tool.
financial_analyst_agent = Agent(
role='Senior Financial Analyst',
goal='Analyze stock data using provided tools and report key prices.',
backstory="You are an experienced financial analyst adept at using data sources to find stock information. You provide clear, direct answers.",
verbose=True,
tools=tools,
# Allowing delegation can be useful, but is not necessary for this simple task.
allow_delegation=False,
)
# --- 3. Refined Task: Clearer Instructions and Error Handling ---
# The task description is more specific and guides the agent on how to react
# to both successful data retrieval and potential errors.
analyze_aapl_task = Task(
description=(
"What is the current simulated stock price for Apple (ticker: AAPL)? "
"Use the 'Stock Price Lookup Tool' to find it. "
"If the ticker is not found, you must report that you were unable to retrieve the price."
),
expected_output=(
"A single, clear sentence stating the simulated stock price for AAPL. "
"For example: 'The simulated stock price for AAPL is $178.15.' "
"If the price cannot be found, state that clearly."
),
agent=financial_analyst_agent,
)
# --- 4. Formulate the Crew ---
# The crew orchestrates how the agent and task work together.
financial_crew = Crew(
agents=[financial_analyst_agent],
tasks=[analyze_aapl_task],
verbose=True # Set to False for less detailed logs in production
)
# --- 5. Run the Crew within a Main Execution Block ---
# Using a __name__ == "__main__": block is a standard Python best practice.
def main():
"""Main function to run the crew."""
# Check for API key before starting to avoid runtime errors.
if not os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"):
print("ERROR: The OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable is not set.")
print("Please set it before running the script.")
return
print("\n## Starting the Financial Crew...")
print("---------------------------------")
# The kickoff method starts the execution.
result = financial_crew.kickoff()
print("\n---------------------------------")
print("## Crew execution finished.")
print("\nFinal Result:\n", result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
|
这段代码演示了一个使用 Crew.ai 库的简单应用,模拟了一个金融分析任务。它定义了一个自定义工具 get_stock_price,模拟查找预定义股票代码的价格。该工具被设计为对有效股票代码返回一个浮点数,对无效代码则引发 ValueError。创建了一个名为 financial_analyst_agent 的 Crew.ai 智能体,其角色为高级金融分析师。该智能体被授予 get_stock_price 工具进行交互。定义了一个任务 analyze_aapl_task,专门指示智能体使用该工具查找 AAPL 的模拟股票价格。任务描述包含了关于如何处理成功和失败两种工具使用情况的清晰指令。组建了一个 Crew(团队),由 financial_analyst_agent 和 analyze_aapl_task 构成。为智能体和 Crew 都启用了 verbose 设置,以便在执行过程中提供详细的日志记录。脚本的主体部分在一个标准的 if __name__ == "__main__": 块内,使用 kickoff() 方法运行 Crew 的任务。在启动 Crew 之前,它会检查是否设置了 OPENAI_API_KEY 环境变量,这是智能体运行所必需的。然后,打印出 Crew 执行的结果,即任务的输出。代码还包括了基本的日志配置,以便更好地跟踪 Crew 的动作和工具调用。它使用了环境变量进行 API 密钥管理,尽管它指出对于生产环境推荐使用更安全的方法。简而言之,核心逻辑展示了如何在 Crew.ai 中定义工具、智能体和任务,以创建协作工作流程。
动手代码示例 (Google ADK)
Google Agent Developer Kit (ADK) 包含一个可直接集成到智能体能力中的原生工具库。
Google 搜索(Google search): 这种组件的主要示例是 Google Search 工具。这个工具作为 Google 搜索引擎的直接接口,赋予智能体执行网络搜索和检索外部信息的功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| from google.adk.agents import Agent as ADKAgent
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
from google.adk.tools import google_search
from google.genai import types
import nest_asyncio
import asyncio
# Define variables required for Session setup and Agent execution
APP_NAME="Google Search_agent"
USER_ID="user1234"
SESSION_ID="1234"
# Define Agent with access to search tool
root_agent = ADKAgent(
name="basic_search_agent",
model="gemini-2.0-flash-exp",
description="Agent to answer questions using Google Search.",
instruction="I can answer your questions by searching the internet. Just ask me anything!",
tools=[google_search] # Google Search is a pre-built tool to perform Google searches.
)
# Agent Interaction
async def call_agent(query):
"""
Helper function to call the agent with a query.
"""
# Session and Runner
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)
runner = Runner(agent=root_agent, app_name=APP_NAME, session_service=session_service)
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
events = runner.run(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
for event in events:
if event.is_final_response():
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("Agent Response: ", final_response)
nest_asyncio.apply()
asyncio.run(call_agent("what's the latest ai news?"))
|
这段代码演示了如何创建和使用一个由 Google ADK for Python 驱动的、利用 Google 搜索工具来回答问题的基础智能体。它定义了应用程序名称、用户 ID 和会话 ID 等常量。创建了一个名为 “basic_search_agent” 的 ADKAgent 实例,并配置它使用 google_search 这一 ADK 提供的预构建工具。代码初始化了一个 InMemorySessionService 来管理会话,并创建了一个 Runner 来执行智能体与会话服务之间的交互。call_agent 异步函数作为辅助函数,用于将用户查询发送给智能体并处理响应。在该函数内部,用户查询被格式化为 types.Content 对象,并通过 runner.run 方法执行。代码遍历返回的事件,查找并打印最终的智能体响应。最后,调用 call_agent 函数并传入查询 “what’s the latest ai news?” 来展示智能体的实际运行。
代码执行(Code execution): Google ADK 功能包括了用于专业任务的集成组件,其中包含一个动态代码执行环境。built_in_code_execution 工具为智能体提供了一个沙盒化的 Python 解释器。这允许模型编写和运行代码来执行计算任务、操作数据结构和执行过程性脚本。这种功能对于解决需要确定性逻辑和精确计算的问题至关重要,这些问题超出了纯粹概率性语言生成的范围。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
| import os, getpass
import asyncio
import nest_asyncio
from typing import List
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import logging
from google.adk.agents import Agent as ADKAgent, LlmAgent
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
from google.adk.tools import google_search
from google.adk.code_executors import BuiltInCodeExecutor
from google.genai import types
# Define variables required for Session setup and Agent execution
APP_NAME="calculator"
USER_ID="user1234"
SESSION_ID="session_code_exec_async"
# Agent Definition
code_agent = LlmAgent(
name="calculator_agent",
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
code_executor=BuiltInCodeExecutor(),
instruction="""You are a calculator agent.
When given a mathematical expression, write and execute Python code to calculate the result.
Return only the final numerical result as plain text, without markdown or code blocks.
""",
description="Executes Python code to perform calculations.",
)
# Agent Interaction (Async)
async def call_agent_async(query):
# Session and Runner
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)
runner = Runner(agent=code_agent, app_name=APP_NAME, session_service=session_service)
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
print(f"\n--- Running Query: {query} ---")
final_response_text = "No final text response captured."
try:
# Use run_async
async for event in runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content):
print(f"Event ID: {event.id}, Author: {event.author}")
# --- Check for specific parts FIRST ---
# has_specific_part = False
if event.content and event.content.parts and event.is_final_response():
for part in event.content.parts: # Iterate through all parts
if part.executable_code:
# Access the actual code string via .code
print(f" Debug: Agent generated code:\n```python\n{part.executable_code.code}\n```")
# has_specific_part = True
elif part.code_execution_result:
# Access outcome and output correctly
print(f" Debug: Code Execution Result: {part.code_execution_result.outcome} - Output:\n{part.code_execution_result.output}")
# has_specific_part = True
# Also print any text parts found in any event for debugging
elif part.text and not part.text.isspace():
print(f" Text: '{part.text.strip()}'")
# Do not set has_specific_part=True here, as we want the final response logic below
# --- Check for final response AFTER specific parts ---
text_parts = [part.text for part in event.content.parts if part.text]
final_result = "".join(text_parts)
print(f"==> Final Agent Response: {final_result}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"ERROR during agent run: {e}")
print("-" * 30)
# Main async function to run the examples
async def main():
await call_agent_async("Calculate the value of (5 + 7) * 3")
await call_agent_async("What is 10 factorial?")
# Execute the main async function
try:
nest_asyncio.apply()
asyncio.run(main())
except RuntimeError as e:
# Handle specific error when running asyncio.run in an already running loop (like Jupyter/Colab)
if "cannot be called from a running event loop" in str(e):
print("\nRunning in an existing event loop (like Colab/Jupyter).")
print("Please run `await main()` in a notebook cell instead.")
# If in an interactive environment like a notebook, you might need to run:
# await main()
else:
raise e # Re-raise other runtime errors
|
这段脚本使用 Google 的 Agent Development Kit (ADK) 创建了一个通过编写和执行 Python 代码来解决数学问题的智能体。它定义了一个 LlmAgent,专门指示其充当计算器,并为其配备了 BuiltInCodeExecutor 工具。主要逻辑位于 call_agent_async 函数中,该函数将用户的查询发送到智能体的运行器,并处理生成的事件。在这个函数内部,一个异步循环遍历事件,打印生成的 Python 代码及其执行结果以进行调试。代码仔细区分了这些中间步骤和包含数值答案的最终事件。最后,一个 main 函数运行智能体,执行两个不同的数学表达式,以展示其执行计算的能力。
企业搜索(Enterprise search): 这段代码定义了一个使用 Google ADK 库的 Python 应用程序。它专门使用 VSearchAgent,该智能体旨在通过搜索指定的 Vertex AI Search 数据存储来回答问题。代码初始化了一个名为 “q2_strategy_vsearch_agent” 的 VSearchAgent,提供了描述、要使用的模型(“gemini-2.0-flash-exp”)和 Vertex AI Search 数据存储的 ID。DATASTORE_ID 预期设置为环境变量。然后,它使用 InMemorySessionService 来管理对话历史,设置了一个 Runner 来运行智能体。定义了一个异步函数 call_vsearch_agent_async 来与智能体交互。该函数接收一个查询,构造一个消息内容对象,并调用运行器的 run_async 方法将查询发送给智能体。然后,该函数会随着智能体响应的到达将其流式传输到控制台。它还会打印最终响应的相关信息,包括来自数据存储的任何来源归属。代码中包含了错误处理,用于捕获智能体执行期间的异常,并提供有关数据存储 ID 不正确或权限缺失等潜在问题的提示信息。另一个异步函数 run_vsearch_example 用于演示如何使用示例查询调用智能体。主执行块会检查 DATASTORE_ID 是否已设置,然后使用 asyncio.run 运行示例。它包含了一个检查,用于处理代码在已存在运行事件循环的环境(如 Jupyter Notebook)中运行的情况。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| import asyncio
from google.genai import types
from google.adk import agents
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
import os
# --- Configuration ---
# Ensure you have set your GOOGLE_API_KEY and DATASTORE_ID environment variables
# For example:
# os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
# os.environ["DATASTORE_ID"] = "YOUR_DATASTORE_ID"
DATASTORE_ID = os.environ.get("DATASTORE_ID")
# --- Application Constants ---
APP_NAME = "vsearch_app"
USER_ID = "user_123" # Example User ID
SESSION_ID = "session_456" # Example Session ID
# --- Agent Definition (Updated with the newer model from the guide) ---
vsearch_agent = agents.VSearchAgent(
name="q2_strategy_vsearch_agent",
description="Answers questions about Q2 strategy documents using Vertex AI Search.",
model="gemini-2.0-flash-exp", # Updated model based on the guide's examples
datastore_id=DATASTORE_ID,
model_parameters={"temperature": 0.0}
)
# --- Runner and Session Initialization ---
runner = Runner(
agent=vsearch_agent,
app_name=APP_NAME,
session_service=InMemorySessionService(),
)
# --- Agent Invocation Logic ---
async def call_vsearch_agent_async(query: str):
"""Initializes a session and streams the agent's response."""
print(f"User: {query}")
print("Agent: ", end="", flush=True)
try:
# Construct the message content correctly
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
# Process events as they arrive from the asynchronous runner
async for event in runner.run_async(
user_id=USER_ID,
session_id=SESSION_ID,
new_message=content
):
# For token-by-token streaming of the response text
if hasattr(event, 'content_part_delta') and event.content_part_delta:
print(event.content_part_delta.text, end="", flush=True)
# Process the final response and its associated metadata
if event.is_final_response():
print() # Newline after the streaming response
if event.grounding_metadata:
print(f" (Source Attributions: {len(event.grounding_metadata.grounding_attributions)} sources found)")
else:
print(" (No grounding metadata found)")
print("-" * 30)
except Exception as e:
print(f"\nAn error occurred: {e}")
print("Please ensure your datastore ID is correct and that the service account has the necessary permissions.")
print("-" * 30)
# --- Run Example ---
async def run_vsearch_example():
# Replace with a question relevant to YOUR datastore content
await call_vsearch_agent_async("Summarize the main points about the Q2 strategy document.")
await call_vsearch_agent_async("What safety procedures are mentioned for lab X?")
# --- Execution ---
if __name__ == "__main__":
if not DATASTORE_ID:
print("Error: DATASTORE_ID environment variable is not set.")
else:
try:
asyncio.run(run_vsearch_example())
except RuntimeError as e:
# This handles cases where asyncio.run is called in an environment
# that already has a running event loop (like a Jupyter notebook).
if "cannot be called from a running event loop" in str(e):
print("Skipping execution in a running event loop. Please run this script directly.")
else:
raise e
|
总而言之,这段代码提供了一个构建对话式 AI 应用程序的基本框架,该应用程序利用 Vertex AI Search 根据存储在数据存储中的信息来回答问题。它演示了如何定义智能体、设置运行器以及在流式传输响应的同时与智能体进行异步交互。重点在于从特定的数据存储中检索和合成信息,以回答用户查询。
Vertex 扩展(Vertex Extensions): Vertex AI 扩展是一个结构化的 API 封装器,它使模型能够连接到外部 API 进行实时数据处理和操作执行。扩展提供了企业级的安全性、数据隐私和性能保证。它们可用于生成和运行代码、查询网站以及分析来自私有数据存储的信息等任务。Google 为常见用例(如代码解释器和 Vertex AI Search)提供了预构建扩展,并可选择创建自定义扩展。扩展的主要优势包括强大的企业控制和与其它 Google 产品的无缝集成。扩展和函数调用之间的关键区别在于它们的执行:Vertex AI 会自动执行扩展,而函数调用需要用户或客户端手动执行。
概要速览(At a Glance)
是什么 (What)
LLM 是强大的文本生成器,但它们从根本上与外部世界是隔离的。它们的知识是静态的,仅限于它们训练时的数据,并且它们缺乏执行动作或检索实时信息的能力。这种固有的局限性阻碍了它们完成需要与外部 API、数据库或服务交互的任务。如果没有通往这些外部系统的桥梁,它们在解决实际问题方面的效用将受到严重限制。
为什么 (Why)
工具使用模式(通常通过函数调用实现)为此问题提供了一个标准化解决方案。它的工作方式是,以 LLM 能够理解的方式描述可用的外部函数或"工具"。根据用户的请求,智能体 LLM 随后可以决定是否需要一个工具,并生成一个结构化数据对象(如 JSON),指定要调用哪个函数以及传入什么参数。一个编排层执行这个函数调用,检索结果,并将其反馈给 LLM。这使得 LLM 能够将最新、外部的信息或动作结果纳入其最终响应中,从而有效地赋予了它行动的能力。
经验法则 (Rule of thumb)
无论何时,只要智能体需要突破 LLM 的内部知识并与外部世界交互,就应使用工具使用模式。这对于需要实时数据(例如,检查天气、股票价格)、访问私有或专有信息(例如,查询公司数据库)、执行精确计算、执行代码,或触发其他系统中的动作(例如,发送电子邮件、控制智能设备)的任务至关重要。
视觉摘要
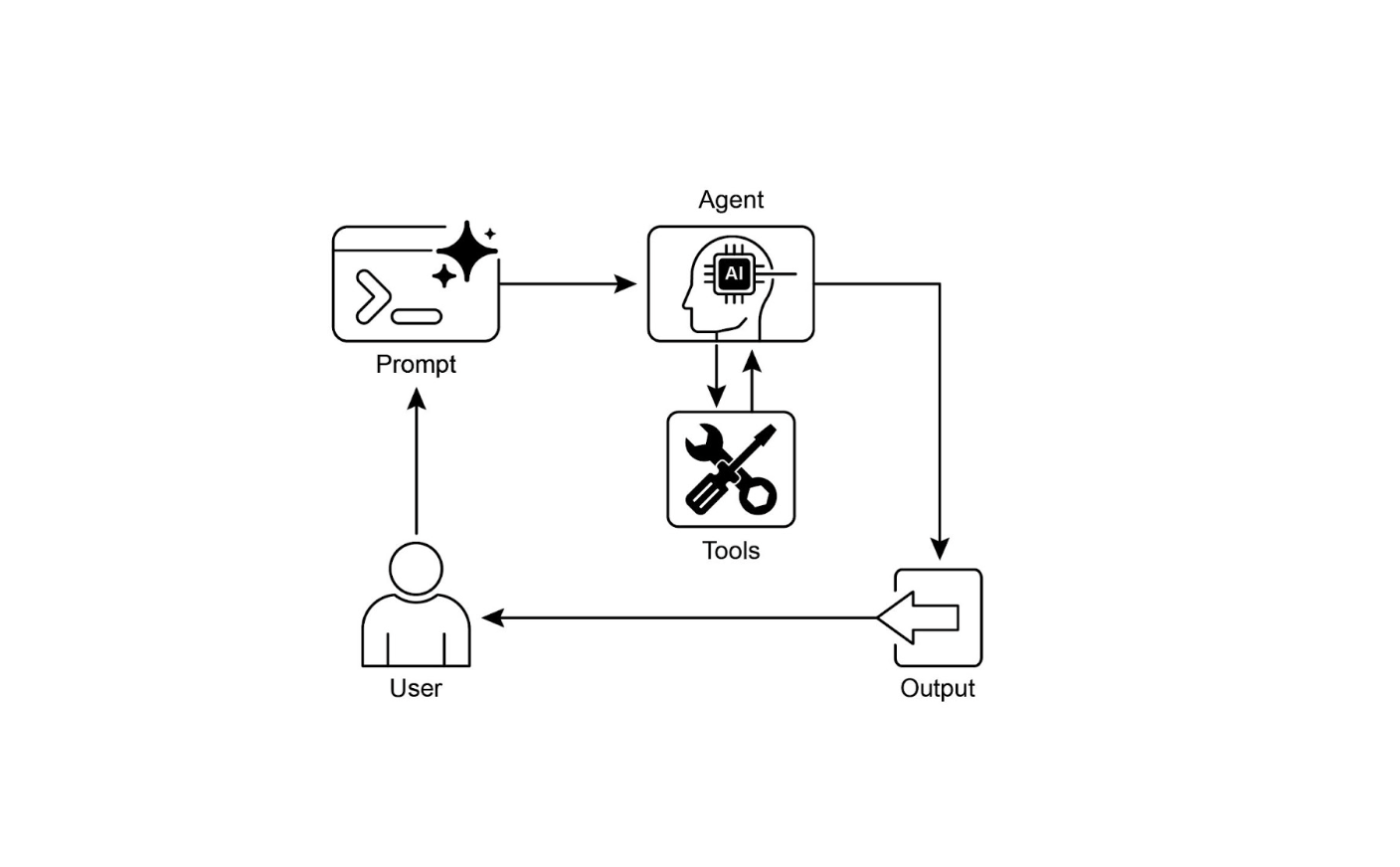
图 2:工具使用设计模式
核心要点 (Key Takeaways)
- 工具使用(函数调用) 允许智能体与外部系统交互并访问动态信息。
- 它涉及以 LLM 能够理解的方式,定义具有清晰描述和参数的工具。
- LLM 决定何时使用工具并生成结构化的函数调用。
- 智能体框架执行实际的工具调用并将结果返回给 LLM。
- 工具使用对于构建能够执行现实世界动作和提供最新信息的智能体至关重要。
- LangChain 使用
@tool 装饰器简化了工具定义,并提供了 create_tool_calling_agent 和 AgentExecutor 来构建使用工具的智能体。 - Google ADK 拥有许多非常有用的预构建工具,如 Google Search、Code Execution 和 Vertex AI Search Tool。
结论
工具使用模式是一个关键的架构原则,它将大型语言模型的功能范围扩展到其内在的文本生成能力之外。通过为模型配备与外部软件和数据源接口的能力,这种范式允许智能体执行动作、进行计算,并从其他系统中检索信息。这个过程涉及模型在确定需要调用外部工具来完成用户查询时,生成一个结构化的请求。像 LangChain、Google ADK 和 Crew AI 这样的框架提供了结构化的抽象和组件,促进了这些外部工具的集成。这些框架管理着向模型展示工具规范以及解析其后续工具使用请求的过程。这简化了复杂智能体系统的开发,使其能够在外部数字环境中进行交互和采取行动。
参考文献 (References)

